Chatbots equipped with artificial intelligence are changing the way we search for information on the Internet. Their conversational interface allows us to have casual conversations, ask questions and get answers naturally as if we were talking to a real person. You don’t have to bother with formulating a simple search term to type into a small Google box. On top of that, we will get a response in the form of text generated by the AI chatbot. Does this mean that the time of search engines like Google Search is coming to an end? Let’s take a look at the capabilities of both technologies.
Chatbot AI as a competitor to Google search – table of contents:
- How is chatbot AI changing how we browse?
- Feature comparison: chatbot AI vs. Google Search
- Speed and availability of information: chatbot AI vs. Google
- Personalization of search results by chatbot AI. Opportunities and threats
- How do chatbot AI handle complex and ambiguous queries?
- The future of search: will chatbot AI dominate?
How is chatbot AI changing how we browse?
AI chatbots, such as ChatGPT created by OpenAI and its close relatives from Microsoft – Bing, Google Bard, or Claude from Anthropic, available in some countries, are changing the approach to information search. Instead of typing keywords and browsing hundreds of links, we can simply ask a question.
For example, we can replace the keyword, “energy saving,” typed into Google’s search engine with a question and AI chat, “What are the best ways to lower your electricity bill?” and immediately get a specific answer generated by AI.
AI chatbots are not only able to acquire the knowledge they have learned in the blink of an eye but also:
- search for information on the Internet – that is, perform the task of a search engine,
- compare them with each other – for example, to confirm their reliability,
- summarize the most important facts – so that we can, for example, based on the recap, choose the article whose content interests us most.
Most notably, AI chatbots can have an interactive conversation, so you can refine the results by asking more questions and receiving personalized advice and ideas.
Feature comparison: chatbot AI vs. Google Search
Comparing specific chatbots with Google Search reveals both common features and significant differences between them.
The most popular ChatGPT in the free version and Claude can generate text answers to natural language questions and conduct simple conversation. However, they do not index websites or give direct links like Google.
Search issues are handled differently by Bing and Bard, two AI chatbots that have access to the Internet.
In Bing, you simply type in any query, from which the search engine “fishes out” words and key phrases and searches the Internet for the information you need. Based on this, it generates a text response with links to sources of information.
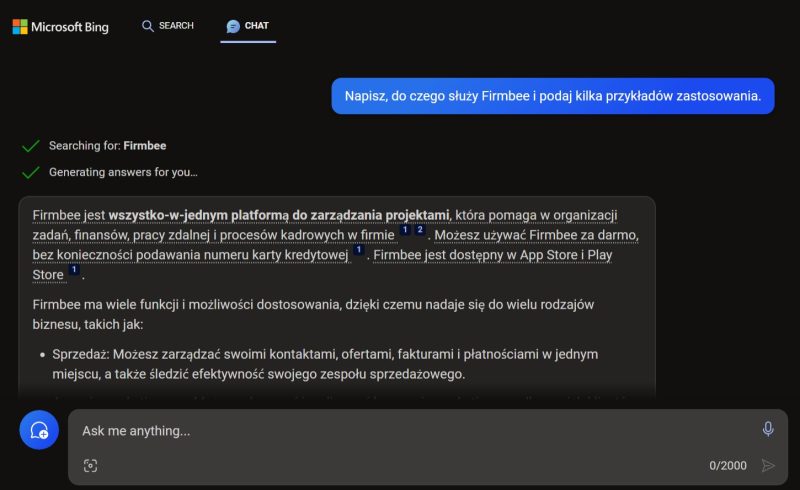
Source: Bing (https://www.bing.com/)
Google Bard first generates an answer with the knowledge it has. Only after clicking on the “G” button, Google it, placed under the AI chat statement does the search begin browsing. In some situations, Bard highlights in green the information in the answer that it managed to confirm during the search. In others, it prompts for search phrases, the clicking of which redirects to the Google search engine.
Google’s search engine itself, on the other hand, offers advanced searches for specific sites and online resources with options for filtering, location, etc. It also displays information in the form of graphics (Knowledge Graph) and allows searching for images and videos. While the way information is displayed is changing dynamically and Google Search is increasingly displaying answers to questions without the need to open links, it does not generate full-text answers like chatbots do.

Source: Google (www.google.pl)
Speed and availability of information: AI chatbots vs. Google
The main advantage of chatbots is instant access to information. This is because they have the potential to deliver information faster than Google Search. Just ask them a question to get an answer right away, without waiting for a page to load or browsing through multiple links.
Of course, Google’s knowledge base is much broader, as it indexes billions of web pages. However, chatbots have increasingly large databases and references, and their answers can be fully sufficient for many popular user queries. Minimal effort in reaching personalized information is their big advantage.
Personalization of search results by chatbot AI. Opportunities and threats
AI chatbots can analyze previous conversations and match results to a specific user. On the one hand, it’s a good chance:
- displaying answers to questions that fit in with even the questioner not fully spoken intention,
- Personalization of the form of the response, such as its length or tone, as well as its content – if I ask about restaurants in the area, and the AI chatbot knows I’m vegan, it will suggest restaurants offering vegan options,
- friendly form of interaction often laced with humor, as well as
- The ability to continue even a long thread on a single topic and easily return to the ongoing conversation.
Unfortunately, the personalization of search results by AI chatbots also poses risks:
- selective content filtering – for example, displaying news not only based on an analysis of our preferences, but also its alignment with a country’s policies,
- The risk of creating “information bubbles” – that is, the chatbot tells us what we already know, what it has told our friends, or what it thought we would like to hear,
- promoting selected products or content – based on combining our preferences with the advertiser’s target audience,
- limiting a variety of sources of information – that is, suggesting what we have already paid attention to.
For example, a chatbot advertising a vacation may show only offers from specific travel agencies, leaving out others. Such personalization can also make certain content completely disappear from the view of our business. For example, if we regularly visit our own company’s website, a chatbot may hide from us… the existence of competitors. Therefore, the transparency of their operation is an important topic.
How do chatbot AI handle complex and ambiguous queries?
AI chatbots sometimes have trouble answering more complex and ambiguous questions that require understanding the relationship between different concepts. They often fail to understand context or nuance, so their answers are sometimes incorrect or incomplete. Therefore, the more precise the question, the better the chatbot’s answer. However, they are getting better at it. For example, after typing a word with a typo, Bing asks an additional question:
- Question, “What is the aquarelle technique?”
- Bing’s answer: “Did you have a watercolor technique in mind?”
At the same time, if a question consists of several interconnected threads, Bing searches for them as separate phrases and then consolidates them into a textual answer.
The future of search: will AI chatbots dominate?
AI chatbots perform much better than search engines on issues that require subjective judgment, advice, or prediction of consequences.
Their development in this direction may bring the greatest benefits. Most likely, however, in the near future, AI chatbots will be a complement rather than a replacement for traditional search engines. We have included their comparison in the table below:
| Understanding natural language | Yes | Yes, but to a limited extent |
| Personalized search results | Yes | Yes, but to a limited extent |
| Ability to refine the results obtained | Yes | Not |
| Search speed | Depends on the chatbot chosen, a few to several seconds | Quick, but sometimes it can take a few seconds |
| Speed of getting an accurate answer to a question | As soon as the search results appear | After independently finding the right answer in the results |
The strengths of AI chatbots are speed, convenience and the ability to generate responses in natural language – written or spoken. But search engines will still be needed when looking for specific sites or online resources.
Key to the development of chatbots will be the reduction of hallucination, that is, generating responses that are plausible but false. Issues of transparency and control over their operation are also key.
If you like our content, join our busy bees community on Facebook, Twitter, LinkedIn, Instagram, YouTube, Pinterest, TikTok.
Author: Robert Whitney
JavaScript expert and instructor who coaches IT departments. His main goal is to up-level team productivity by teaching others how to effectively cooperate while coding.
AI in business:
- Threats and opportunities of AI in business (part 1)
- Threats and opportunities of AI in business (part 2)
- AI applications in business - overview
- AI-assisted text chatbots
- Business NLP today and tomorrow
- The role of AI in business decision-making
- Scheduling social media posts. How can AI help?
- Automated social media posts
- New services and products operating with AI
- What are the weaknesses of my business idea? A brainstorming session with ChatGPT
- Using ChatGPT in business
- Synthetic actors. Top 3 AI video generators
- 3 useful AI graphic design tools. Generative AI in business
- 3 awesome AI writers you must try out today
- Exploring the power of AI in music creation
- Navigating new business opportunities with ChatGPT-4
- AI tools for the manager
- 6 awesome ChatGTP plugins that will make your life easier
- 3 grafików AI. Generatywna sztuczna inteligencja dla biznesu
- What is the future of AI according to McKinsey Global Institute?
- Artificial intelligence in business - Introduction
- What is NLP, or natural language processing in business
- Automatic document processing
- Google Translate vs DeepL. 5 applications of machine translation for business
- The operation and business applications of voicebots
- Virtual assistant technology, or how to talk to AI?
- What is Business Intelligence?
- Will artificial intelligence replace business analysts?
- How can artificial intelligence help with BPM?
- AI and social media – what do they say about us?
- Artificial intelligence in content management
- Creative AI of today and tomorrow
- Multimodal AI and its applications in business
- New interactions. How is AI changing the way we operate devices?
- RPA and APIs in a digital company
- The future job market and upcoming professions
- AI in EdTech. 3 examples of companies that used the potential of artificial intelligence
- Artificial intelligence and the environment. 3 AI solutions to help you build a sustainable business
- AI content detectors. Are they worth it?
- ChatGPT vs Bard vs Bing. Which AI chatbot is leading the race?
- Is chatbot AI a competitor to Google search?
- Effective ChatGPT Prompts for HR and Recruitment
- Prompt engineering. What does a prompt engineer do?
- AI Mockup generator. Top 4 tools
- AI and what else? Top technology trends for business in 2024
- AI and business ethics. Why you should invest in ethical solutions
- Meta AI. What should you know about Facebook and Instagram's AI-supported features?
- AI regulation. What do you need to know as an entrepreneur?
- 5 new uses of AI in business
- AI products and projects - how are they different from others?
- AI-assisted process automation. Where to start?
- How do you match an AI solution to a business problem?
- AI as an expert on your team
- AI team vs. division of roles
- How to choose a career field in AI?
- Is it always worth it to add artificial intelligence to the product development process?
- AI in HR: How recruitment automation affects HR and team development
- 6 most interesting AI tools in 2023
- 6 biggest business mishaps caused by AI
- What is the company's AI maturity analysis?
- AI for B2B personalization
- ChatGPT use cases. 18 examples of how to improve your business with ChatGPT in 2024
- Microlearning. A quick way to get new skills
- The most interesting AI implementations in companies in 2024
- What do artificial intelligence specialists do?
- What challenges does the AI project bring?
- Top 8 AI tools for business in 2024
- AI in CRM. What does AI change in CRM tools?
- The UE AI Act. How does Europe regulate the use of artificial intelligence
- Sora. How will realistic videos from OpenAI change business?
- Top 7 AI website builders
- No-code tools and AI innovations
- How much does using AI increase the productivity of your team?
- How to use ChatGTP for market research?
- How to broaden the reach of your AI marketing campaign?
- "We are all developers". How can citizen developers help your company?
- AI in transportation and logistics
- What business pain points can AI fix?
- Artificial intelligence in the media
- AI in banking and finance. Stripe, Monzo, and Grab
- AI in the travel industry
- How AI is fostering the birth of new technologies
- The revolution of AI in social media
- AI in e-commerce. Overview of global leaders
- Top 4 AI image creation tools
- Top 5 AI tools for data analysis
- AI strategy in your company - how to build it?
- Best AI courses – 6 awesome recommendations
- Optimizing social media listening with AI tools
- IoT + AI, or how to reduce energy costs in a company
- AI in logistics. 5 best tools
- GPT Store – an overview of the most interesting GPTs for business
- LLM, GPT, RAG... What do AI acronyms mean?
- AI robots – the future or present of business?
- What is the cost of implementing AI in a company?
- How can AI help in a freelancer’s career?
- Automating work and increasing productivity. A guide to AI for freelancers
- AI for startups – best tools
- Building a website with AI
- OpenAI, Midjourney, Anthropic, Hugging Face. Who is who in the world of AI?
- Eleven Labs and what else? The most promising AI startups
- Synthetic data and its importance for the development of your business
- Top AI search engines. Where to look for AI tools?
- Video AI. The latest AI video generators
- AI for managers. How AI can make your job easier
- What’s new in Google Gemini? Everything you need to know
- AI in Poland. Companies, meetings, and conferences
- AI calendar. How to optimize your time in a company?
- AI and the future of work. How to prepare your business for change?
- AI voice cloning for business. How to create personalized voice messages with AI?
- Fact-checking and AI hallucinations
- AI in recruitment – developing recruitment materials step-by-step
- Midjourney v6. Innovations in AI image generation
- AI in SMEs. How can SMEs compete with giants using AI?
- How is AI changing influencer marketing?
- Is AI really a threat to developers? Devin and Microsoft AutoDev
- AI chatbots for e-commerce. Case studies
- Best AI chatbots for ecommerce. Platforms
- How to stay on top of what's going on in the AI world?
- Taming AI. How to take the first steps to apply AI in your business?
- Perplexity, Bing Copilot, or You.com? Comparing AI search engines
- ReALM. A groundbreaking language model from Apple?
- AI experts in Poland
- Google Genie — a generative AI model that creates fully interactive worlds from images
- Automation or augmentation? Two approaches to AI in a company
- LLMOps, or how to effectively manage language models in an organization
- AI video generation. New horizons in video content production for businesses
- Best AI transcription tools. How to transform long recordings into concise summaries?
- Sentiment analysis with AI. How does it help drive change in business?
- The role of AI in content moderation


















