Can you imagine a company where most processes work without human intervention? Reports generate themselves, invoices are issued by robots, and customer inquiries are handled by intelligent chatbots. It sounds futuristic, but thanks to hyperautomation it is becoming more and more real.
Hyperautomation – table of contents:
The global hyper-automation market was worth about $9 billion in 2021. It is expected to grow to about $26.5 billion by 2028, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of about 23.5% between 2022 and 2028. This significant growth is the result of practical, business applications of hyperautomation. From transforming everyday tasks to revolutionizing management, hyper-automation is the key to a future-oriented, automated business environment.
What is hyperautomation?
Hyper-automation is the concept of holistic automation of a company’s processes using advanced technologies. It includes, but is not limited to:
- Robotization of business processes (Robotic Process Automation, RPA),
- Application Programming Interfaces (APIs),
- Artificial Intelligence (AI),
- Machine Learning (ML), and
- Natural Language Processing (NLP) technologies.
Its goal is to reduce the need for human intervention in repetitive tasks in favor of focusing on creative work and building competitive advantage.
The main advantages of hyperautomation are:
- reducing the cost of company operations,
- saving time and human resources,
- error elimination,
- greater flexibility,
- significant scalability of operations and
- improving the quality of customer service.
Nonetheless, challenges such as high initial investment costs or the need for specialized knowledge can be a barrier for many companies.
Hyperautomation vs. automation
Hyperautomation differs from traditional automation in scale and scope. While automation focuses on single tasks, hyperautomation encompasses a company’s entire processes and ecosystem and aims for a comprehensive digital transformation rather than a point improvement in the efficiency of a company’s operations.
Automation
Automation refers to the use of technology to minimize or eliminate the manual performance of repetitive tasks and processes. Tools such as make.com or Zapier enable automation of tasks, such as moving data between different applications, generating notifications or scheduling tasks. For example, Zapier can automatically update a spreadsheet in Google Sheets when a new entry is added in Google Forms.

Source: make.com (https://www.make.com/)
Hyperautomation
Hyperautomation, on the other hand, is a more advanced form of automation that integrates various technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI), robotic process automation (RPA), and application programming interfaces (APIs) to create a system that can automatically manage and optimize complex, multi-step business processes.
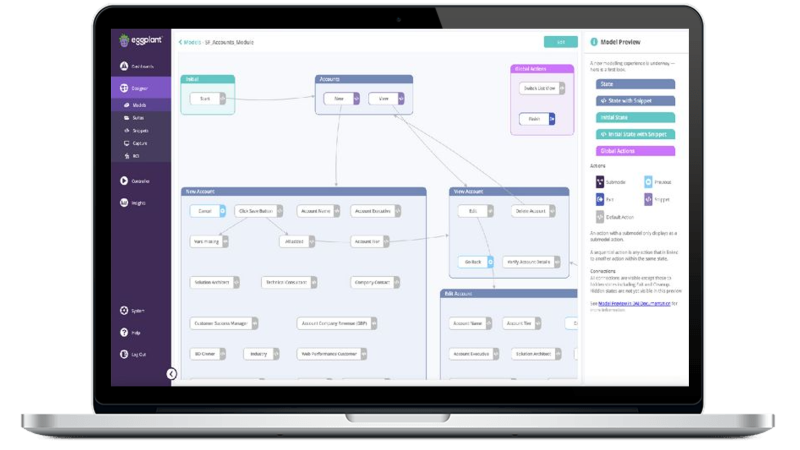
Source: Keysight (https://www.keysight.com)
Hyperautomation features tools such as RPA platforms to integrate with various systems via APIs to automate a wide range of tasks and processes.
Hyperautomation applications in business
Hyperautomation applications in business include, but are not limited to:
- HR and recruitment – robots analyze recruitment documents such as resumes and cover letters, and then pre-screen candidates automatically, schedule recruitment appointments and send notifications. For example, Santander Bank has implemented a fully digital recruitment process based on hyperautomation,
- Finance and accounting – a combination of RPA and API capabilities along with artificial intelligence allows automating the entire process of generating reports and invoices, posting documents, and verifying payments,
- Manufacturing and supply chain – the industry applies hyperautomation for inventory monitoring, production scheduling, automated reporting, among other things, which reduces downtime and improves on-time delivery.
How to implement hyperautomation?
Implementing hyperautomation in a medium-sized company can become a complicated process that requires careful planning and execution. Here are steps that can help you organize and execute it:
- Analysis of the current state – at the outset, you need to identify and evaluate the current business and technological processes to be automated. Understanding what technologies are currently in use and identifying areas that can be improved with hyper-automation is key to its successful implementation.
- Defining goals – the second step of setting specific, measurable goals that you want to achieve by implementing hyper-automation, such as increasing efficiency, reducing errors, or improving customer service.
- Technology selection – Equally important is the selection of appropriate technologies for implementation, such as robotic process automation (RPA) tools, artificial intelligence (AI), and application programming interfaces (APIs).
- Process design – not all processes operating in the company are worth automating one to one, in all likelihood, you will need to develop new processes and procedures that will be automated and integrated through selected technologies.
- Development and testing – building, configuring and testing a hyperautomation system to make sure it meets requirements and achieves its intended goals is a lengthy process that must involve both hyperautomation specialists and the company’s team.
- Team training – training the employees who will be working with the new system so that they understand how to use it and how they can use it in their daily work.
- Implementation – putting the hyperautomation system into practice, monitoring its performance and resolving any problems that may arise during implementation.
- Optimization– Regular monitoring of the hyper-automation system’s performance and making improvements, as well as reporting problems and resolving them on an ongoing basis, are necessary to make sure the hyper-automation system continues to contribute to business goals.
Implementing hyperautomation is a long-term process that requires a significant commitment of management teams and resources. When properly planned and implemented, hyper-automation can make a significant contribution to improving efficiency and innovation in a company.
Hyperautomation technologies – API and RPA
Robotic process automation (RPA) is a technology that allows tedious, repetitive tasks to be automated with “robots” that can mimic the actions of humans in operating applications. In its basic form, RPA can, for example, copy text from a selected browser window and paste it into a spreadsheet. When RPA is equipped with artificial intelligence, it can handle very complex processes, selecting appropriate actions depending on the result obtained in a given step. With RPA, processes such as claims handling can be automated, speeding up customer response and saving staff time.
On the other hand, application programming interfaces (APIs) enable communication between different applications and systems at the code level. APIs feature the exchange of data between different systems in a programmable way. For example, generating Google documents based on data from other systems can be helpful in scenarios such as automatic invoice creation in e-commerce companies.
The combination of RPA and API can offer the best of both worlds, allowing both surface and deep automation, leading to greater efficiency and flexibility in business process automation. This hybrid approach can become particularly beneficial in complex business environments where different systems and processes must be integrated for maximum operational efficiency.
Summary
Hyperautomation is undoubtedly one of the most promising and disruptive concepts in business process automation in recent years. Combining the potential of advanced technologies such as RPA and APIs, complemented by artificial intelligence and machine learning, it opens up opportunities for companies to reduce costs and improve operational efficiency. Indeed, its goal is the holistic digital transformation of the company by eliminating the need for manual handling of repetitive tasks.
Hyperautomation differs from traditional automation in scale – as it involves entire processes rather than individual tasks. It saves costs, time and human resources, and reduces errors.
It has wide applications in business and can be implemented in customer service, HR, finance or supply chain. However, to do so, the transformation process needs to be carefully analyzed and planned. Although the implementation of hyperautomation is not easy, and a fully automated company is still in the realm of science fiction, certainly, hyper-automation will soon become an everyday reality of modern business.
Hyperautomation has the potential to revolutionize the functioning of modern companies, but it requires a careful and gradual introduction to maintain a balance between human and machine work. Its full potential can be realized by skillfully combining different technologies.
If you like our content, join our busy bees community on Facebook, Twitter, LinkedIn, Instagram, YouTube, Pinterest, TikTok.
Author: Robert Whitney
JavaScript expert and instructor who coaches IT departments. His main goal is to up-level team productivity by teaching others how to effectively cooperate while coding.
AI in business:
- Threats and opportunities of AI in business (part 1)
- Threats and opportunities of AI in business (part 2)
- AI applications in business - overview
- AI-assisted text chatbots
- Business NLP today and tomorrow
- The role of AI in business decision-making
- Scheduling social media posts. How can AI help?
- Automated social media posts
- New services and products operating with AI
- What are the weaknesses of my business idea? A brainstorming session with ChatGPT
- Using ChatGPT in business
- Synthetic actors. Top 3 AI video generators
- 3 useful AI graphic design tools. Generative AI in business
- 3 awesome AI writers you must try out today
- Exploring the power of AI in music creation
- Navigating new business opportunities with ChatGPT-4
- AI tools for the manager
- 6 awesome ChatGTP plugins that will make your life easier
- 3 grafików AI. Generatywna sztuczna inteligencja dla biznesu
- What is the future of AI according to McKinsey Global Institute?
- Artificial intelligence in business - Introduction
- What is NLP, or natural language processing in business
- Automatic document processing
- Google Translate vs DeepL. 5 applications of machine translation for business
- The operation and business applications of voicebots
- Virtual assistant technology, or how to talk to AI?
- What is Business Intelligence?
- Will artificial intelligence replace business analysts?
- How can artificial intelligence help with BPM?
- AI and social media – what do they say about us?
- Artificial intelligence in content management
- Creative AI of today and tomorrow
- Multimodal AI and its applications in business
- New interactions. How is AI changing the way we operate devices?
- RPA and APIs in a digital company
- The future job market and upcoming professions
- AI in EdTech. 3 examples of companies that used the potential of artificial intelligence
- Artificial intelligence and the environment. 3 AI solutions to help you build a sustainable business
- AI content detectors. Are they worth it?
- ChatGPT vs Bard vs Bing. Which AI chatbot is leading the race?
- Is chatbot AI a competitor to Google search?
- Effective ChatGPT Prompts for HR and Recruitment
- Prompt engineering. What does a prompt engineer do?
- AI Mockup generator. Top 4 tools
- AI and what else? Top technology trends for business in 2024
- AI and business ethics. Why you should invest in ethical solutions
- Meta AI. What should you know about Facebook and Instagram's AI-supported features?
- AI regulation. What do you need to know as an entrepreneur?
- 5 new uses of AI in business
- AI products and projects - how are they different from others?
- AI-assisted process automation. Where to start?
- How do you match an AI solution to a business problem?
- AI as an expert on your team
- AI team vs. division of roles
- How to choose a career field in AI?
- Is it always worth it to add artificial intelligence to the product development process?
- AI in HR: How recruitment automation affects HR and team development
- 6 most interesting AI tools in 2023
- 6 biggest business mishaps caused by AI
- What is the company's AI maturity analysis?
- AI for B2B personalization
- ChatGPT use cases. 18 examples of how to improve your business with ChatGPT in 2024
- Microlearning. A quick way to get new skills
- The most interesting AI implementations in companies in 2024
- What do artificial intelligence specialists do?
- What challenges does the AI project bring?
- Top 8 AI tools for business in 2024
- AI in CRM. What does AI change in CRM tools?
- The UE AI Act. How does Europe regulate the use of artificial intelligence
- Sora. How will realistic videos from OpenAI change business?
- Top 7 AI website builders
- No-code tools and AI innovations
- How much does using AI increase the productivity of your team?
- How to use ChatGTP for market research?
- How to broaden the reach of your AI marketing campaign?
- "We are all developers". How can citizen developers help your company?
- AI in transportation and logistics
- What business pain points can AI fix?
- Artificial intelligence in the media
- AI in banking and finance. Stripe, Monzo, and Grab
- AI in the travel industry
- How AI is fostering the birth of new technologies
- The revolution of AI in social media
- AI in e-commerce. Overview of global leaders
- Top 4 AI image creation tools
- Top 5 AI tools for data analysis
- AI strategy in your company - how to build it?
- Best AI courses – 6 awesome recommendations
- Optimizing social media listening with AI tools
- IoT + AI, or how to reduce energy costs in a company
- AI in logistics. 5 best tools
- GPT Store – an overview of the most interesting GPTs for business
- LLM, GPT, RAG... What do AI acronyms mean?
- AI robots – the future or present of business?
- What is the cost of implementing AI in a company?
- How can AI help in a freelancer’s career?
- Automating work and increasing productivity. A guide to AI for freelancers
- AI for startups – best tools
- Building a website with AI
- OpenAI, Midjourney, Anthropic, Hugging Face. Who is who in the world of AI?
- Eleven Labs and what else? The most promising AI startups
- Synthetic data and its importance for the development of your business
- Top AI search engines. Where to look for AI tools?
- Video AI. The latest AI video generators
- AI for managers. How AI can make your job easier
- What’s new in Google Gemini? Everything you need to know
- AI in Poland. Companies, meetings, and conferences
- AI calendar. How to optimize your time in a company?
- AI and the future of work. How to prepare your business for change?
- AI voice cloning for business. How to create personalized voice messages with AI?
- Fact-checking and AI hallucinations
- AI in recruitment – developing recruitment materials step-by-step
- Midjourney v6. Innovations in AI image generation
- AI in SMEs. How can SMEs compete with giants using AI?
- How is AI changing influencer marketing?
- Is AI really a threat to developers? Devin and Microsoft AutoDev
- AI chatbots for e-commerce. Case studies
- Best AI chatbots for ecommerce. Platforms
- How to stay on top of what's going on in the AI world?
- Taming AI. How to take the first steps to apply AI in your business?
- Perplexity, Bing Copilot, or You.com? Comparing AI search engines
- ReALM. A groundbreaking language model from Apple?
- AI experts in Poland
- Google Genie — a generative AI model that creates fully interactive worlds from images
- Automation or augmentation? Two approaches to AI in a company
- LLMOps, or how to effectively manage language models in an organization
- AI video generation. New horizons in video content production for businesses
- Best AI transcription tools. How to transform long recordings into concise summaries?
- Sentiment analysis with AI. How does it help drive change in business?
- The role of AI in content moderation


















