AI is playing a key role in the transformation of social media, from automated content moderation to personalized recommendations and advertising. According to Statista, the number of active social media users worldwide was 4.26 billion in 2021, and the average time spent on social media was 2 hours and 27 minutes per day. As the number of social media users grows, so does the demand for AI solutions to help understand customer preferences. The social media AI market is expected to reach $3,714.89 million by 2026, an increase of 28.77%
AI in social media – table of contents:
AI in social media analytics
What is the great need for AI tools to analyze the behavior of people through social media? It’s primarily about understanding, as well as predicting, user behavior on social media platforms. This is difficult because of the amount and types of data being acquired. An analyst not supported by AI in social media can count reactions and the number of comments, or assess whether posts are positive or negative. The task will be tedious and error-prone.
On the other hand, an analyst with AI’s help in social media will gain the ability to gather data from all the places where company mentions appear, as well as get information about where they should be in the future. This is possible because AI can operate on a much larger scale. In other words, it can analyze Big Data, i.e. huge amounts of disparate data.
How to exploit data collected by AI in social media?
AI-based tools in social media enable us to reflect on associations, showing the relationships linking a product’s name to adjectives describing quality, emotions or associated values. This can prove to be a key tool for social media analysis, showing how customers perceive our business. Linking the frequency of certain words, combining them with photos and users’ emotional reactions – opens up entirely new business opportunities.
Planning posts with AI in social media
By automating the publication calendar of social media content with AI, we can plan the date and time each post will appear. If the AI tool of choice is equipped with a learning artificial intelligence module, we can choose to entrust automation to optimize the publication calendar. Having data on the popularity of previous posts, an application such as Buffer will suggest when it’s best to publish the next post.
Can AI create social media posts on its own?
Fully automated social media posts are primarily effective for content repurposing, that is:
- reuse of existing content,
- matching it to the requirements of publication in other social media,
- optimization of entries for SEO and
- automatically finding the “guiding thread” connecting the materials to make them consistent.
Given the level of sophistication of ChatGPT or Google Bard, which can generate long, meaningful statements, and adding in advanced image generators such as Dalle-2, Midjourney or Stable Diffusion, the answer to whether AI can create social media posts on its own is yes.
There is one condition: to keep the post in the style of our previous contributions and continue the topics you cover on social media, you must have appropriate prompts. In addition, the source material – that is, the context provided to AI – must include enough examples of your previous publications. And if what you want to write about is not publicly available, you also need to provide information directly relevant to the topic. In other words, it will not be full automation, but rather collaboration with AI.
3 AI tools for social media marketing
If you want to outsource the writing or development of your company’s social media publishing calendar to a tool that works with artificial intelligence, there are three worth looking into. Cortex is a tool for optimizing and personalizing marketing content, Lately is for creating content strategies and ideas and Buffer is mainly for managing calendars and social media collaborations. All of these tools feature AI to increase engagement and return on investment in social media marketing.
Cortex
Cortex is an AI tool that helps companies increase their return on investment in social media marketing by:
- consolidation of tools,
- automation of repetitive tasks,
- adding data to analytical tools.
Cortex analyzes marketing content and predicts how consumers will respond to it. It also leverages existing content, generates new posts linking to predetermined pages or documents as well as answers customer questions in real-time. Cortex also offers the ability to apply selected filters to images so that they are consistent with the brand’s color scheme, automatically match colors and monitor competitors.
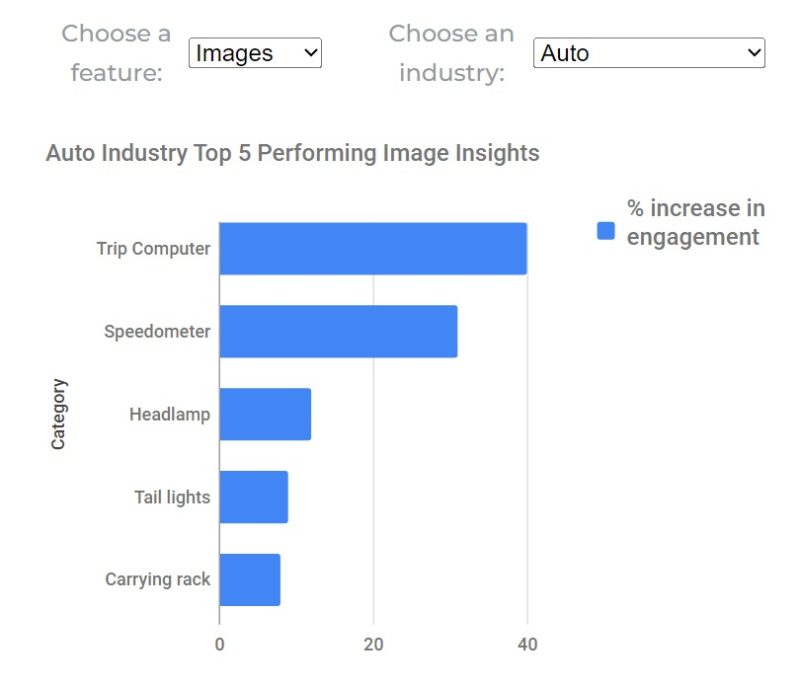
Source: www.meetcortex.com
Buffer
Buffer is a social media marketing tool that helps small businesses build their audience organically. One of the interesting features is Buffer AI Assistant, which:
- helps generate content ideas,
- enables reuse of existing content,
- creates instant responses to comments, as well as
- allows you to generate variations of posts.
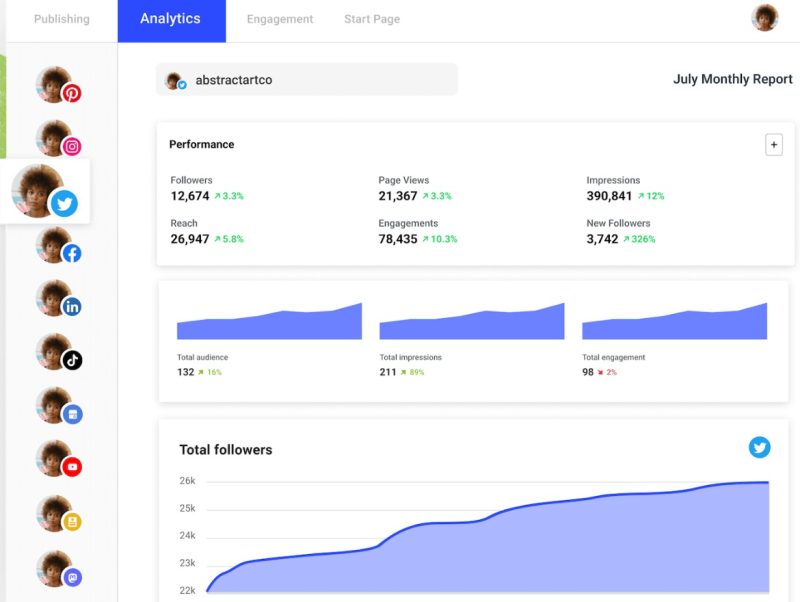
Source: buffer.com
Lately
Lately is a social selling platform that applies artificial intelligence to deliver marketing content. Lately also offers a special tool to reuse existing content to increase engagement across all social platforms.
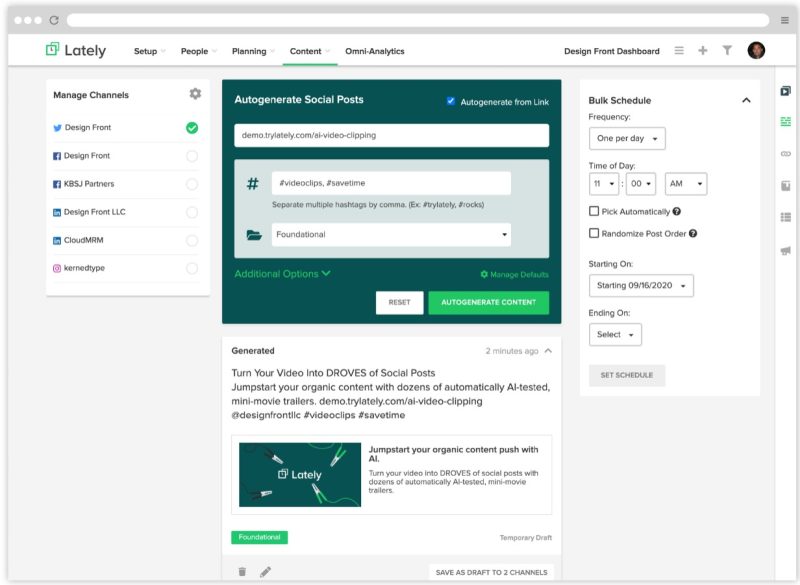
Source: lately.ai
Here are some of their main differences and how AI is used in these tools:
- Cortex employs AI to analyze marketing content and predict consumer response, as well as tailor content for various social media platforms, optimize it for SEO and monitor competition.
- Lately applies AI to create marketing strategies and generate content ideas. It learns a brand’s voice and turns existing content into effective social media posts.
- Buffer uses AI to schedule publications on various platforms, including TiTikTok creates instant responses and variations of posts.
AI in social media – summary
AI tools help improve the effectiveness of marketing on social media platforms, including creating textual and visual content, monitoring social media or managing ads. However, the best results will be achieved by using AI in social media as an assistant to help improve the quality of published content and optimize the calendar, rather than as an automated post-creation machine. Running a company’s social media can be significantly helped by keeping a close eye on analytics and drawing conclusions, especially with the help of AI.
If you like our content, join our busy bees community on Facebook, Twitter, LinkedIn, Instagram, YouTube, Pinterest.
Author: Robert Whitney
JavaScript expert and instructor who coaches IT departments. His main goal is to up-level team productivity by teaching others how to effectively cooperate while coding.
AI in business:
- Threats and opportunities of AI in business (part 1)
- Threats and opportunities of AI in business (part 2)
- AI applications in business - overview
- AI-assisted text chatbots
- Business NLP today and tomorrow
- The role of AI in business decision-making
- Scheduling social media posts. How can AI help?
- Automated social media posts
- New services and products operating with AI
- What are the weaknesses of my business idea? A brainstorming session with ChatGPT
- Using ChatGPT in business
- Synthetic actors. Top 3 AI video generators
- 3 useful AI graphic design tools. Generative AI in business
- 3 awesome AI writers you must try out today
- Exploring the power of AI in music creation
- Navigating new business opportunities with ChatGPT-4
- AI tools for the manager
- 6 awesome ChatGTP plugins that will make your life easier
- 3 grafików AI. Generatywna sztuczna inteligencja dla biznesu
- What is the future of AI according to McKinsey Global Institute?
- Artificial intelligence in business - Introduction
- What is NLP, or natural language processing in business
- Automatic document processing
- Google Translate vs DeepL. 5 applications of machine translation for business
- The operation and business applications of voicebots
- Virtual assistant technology, or how to talk to AI?
- What is Business Intelligence?
- Will artificial intelligence replace business analysts?
- How can artificial intelligence help with BPM?
- AI and social media – what do they say about us?
- Artificial intelligence in content management
- Creative AI of today and tomorrow
- Multimodal AI and its applications in business
- New interactions. How is AI changing the way we operate devices?
- RPA and APIs in a digital company
- The future job market and upcoming professions
- AI in EdTech. 3 examples of companies that used the potential of artificial intelligence
- Artificial intelligence and the environment. 3 AI solutions to help you build a sustainable business
- AI content detectors. Are they worth it?
- ChatGPT vs Bard vs Bing. Which AI chatbot is leading the race?
- Is chatbot AI a competitor to Google search?
- Effective ChatGPT Prompts for HR and Recruitment
- Prompt engineering. What does a prompt engineer do?
- AI Mockup generator. Top 4 tools
- AI and what else? Top technology trends for business in 2024
- AI and business ethics. Why you should invest in ethical solutions
- Meta AI. What should you know about Facebook and Instagram's AI-supported features?
- AI regulation. What do you need to know as an entrepreneur?
- 5 new uses of AI in business
- AI products and projects - how are they different from others?
- AI-assisted process automation. Where to start?
- How do you match an AI solution to a business problem?
- AI as an expert on your team
- AI team vs. division of roles
- How to choose a career field in AI?
- Is it always worth it to add artificial intelligence to the product development process?
- AI in HR: How recruitment automation affects HR and team development
- 6 most interesting AI tools in 2023
- 6 biggest business mishaps caused by AI
- What is the company's AI maturity analysis?
- AI for B2B personalization
- ChatGPT use cases. 18 examples of how to improve your business with ChatGPT in 2024
- Microlearning. A quick way to get new skills
- The most interesting AI implementations in companies in 2024
- What do artificial intelligence specialists do?
- What challenges does the AI project bring?
- Top 8 AI tools for business in 2024
- AI in CRM. What does AI change in CRM tools?
- The UE AI Act. How does Europe regulate the use of artificial intelligence
- Sora. How will realistic videos from OpenAI change business?
- Top 7 AI website builders
- No-code tools and AI innovations
- How much does using AI increase the productivity of your team?
- How to use ChatGTP for market research?
- How to broaden the reach of your AI marketing campaign?
- "We are all developers". How can citizen developers help your company?
- AI in transportation and logistics
- What business pain points can AI fix?
- Artificial intelligence in the media
- AI in banking and finance. Stripe, Monzo, and Grab
- AI in the travel industry
- How AI is fostering the birth of new technologies
- The revolution of AI in social media
- AI in e-commerce. Overview of global leaders
- Top 4 AI image creation tools
- Top 5 AI tools for data analysis
- AI strategy in your company - how to build it?
- Best AI courses – 6 awesome recommendations
- Optimizing social media listening with AI tools
- IoT + AI, or how to reduce energy costs in a company
- AI in logistics. 5 best tools
- GPT Store – an overview of the most interesting GPTs for business
- LLM, GPT, RAG... What do AI acronyms mean?
- AI robots – the future or present of business?
- What is the cost of implementing AI in a company?
- How can AI help in a freelancer’s career?
- Automating work and increasing productivity. A guide to AI for freelancers
- AI for startups – best tools
- Building a website with AI
- OpenAI, Midjourney, Anthropic, Hugging Face. Who is who in the world of AI?
- Eleven Labs and what else? The most promising AI startups
- Synthetic data and its importance for the development of your business
- Top AI search engines. Where to look for AI tools?
- Video AI. The latest AI video generators
- AI for managers. How AI can make your job easier
- What’s new in Google Gemini? Everything you need to know
- AI in Poland. Companies, meetings, and conferences
- AI calendar. How to optimize your time in a company?
- AI and the future of work. How to prepare your business for change?
- AI voice cloning for business. How to create personalized voice messages with AI?
- Fact-checking and AI hallucinations
- AI in recruitment – developing recruitment materials step-by-step
- Midjourney v6. Innovations in AI image generation
- AI in SMEs. How can SMEs compete with giants using AI?
- How is AI changing influencer marketing?
- Is AI really a threat to developers? Devin and Microsoft AutoDev
- AI chatbots for e-commerce. Case studies
- Best AI chatbots for ecommerce. Platforms
- How to stay on top of what's going on in the AI world?
- Taming AI. How to take the first steps to apply AI in your business?
- Perplexity, Bing Copilot, or You.com? Comparing AI search engines
- ReALM. A groundbreaking language model from Apple?
- AI experts in Poland
- Google Genie — a generative AI model that creates fully interactive worlds from images
- Automation or augmentation? Two approaches to AI in a company
- LLMOps, or how to effectively manage language models in an organization
- AI video generation. New horizons in video content production for businesses
- Best AI transcription tools. How to transform long recordings into concise summaries?
- Sentiment analysis with AI. How does it help drive change in business?
- The role of AI in content moderation


















