The choice of project management methods is often imposed by the organization, which does not leave the Project Manager a free hand when it comes to how to plan and frame the implementation of the tasks included in the project. However, it sometimes happens that we can choose project management methods ourselves, or enrich the activities with elements taken from other methods.
Project management methods – table of contents:
- Project management methods – introduction
- Scrum
- Kanban
- Scrumban
- Extreme programming (XP)
- Lean
- Prince2
- Six Sigma
- Critical path method (CPM
- Critical chain method (CCPM)
- Summary
Project management methods – introduction
In the following text, we continue our presentation of project management methods and look at another way organizations practice project implementation.
Scrum
Scrum is the most popular way of agile project team management. According to the 2021 15th Annual State Of Agile report, Scrum is now used for 66% of projects. Although it was developed for software development, it has quickly gained popularity among teams with other specialties. It is used by HR and marketing departments, financiers and designers.
The main advantage of Scrum is intensive communication and continuous improvement of team cooperation and maximizing team motivation and efficiency. It works best for one-off tasks that require an innovative approach.
On the other hand, among the disadvantages of Scrum are the specific terminology and the generality of the principles, which are easier to learn than to apply in practice. Thus, one should get prepared to absorb a large dose of terminology, understand who the Scrum Master and Product Owner are, and what a Sprint and its Retrospective are all about. However, the measurable successes achieved by teams managed with Scrum make up for these minor inconveniences.
Kanban
According to the State Of Agile report mentioned above, 7% of teams are managed using Kanban. It is better suited than Scrum for continuous and repetitive tasks that do not need to plan in great detail. On the other hand, its main feature concerns focus on timeliness and quality of delivered results.
The Project Manager’s job is to create a queue of tasks, from which each team member chooses the ones he or she will do first. The biggest advantage of Kanban is the clear visualization of the project status. It is from Kanban boards that Kanban got its name. They divide tasks into a queue of work to be done, those in progress and those already done.
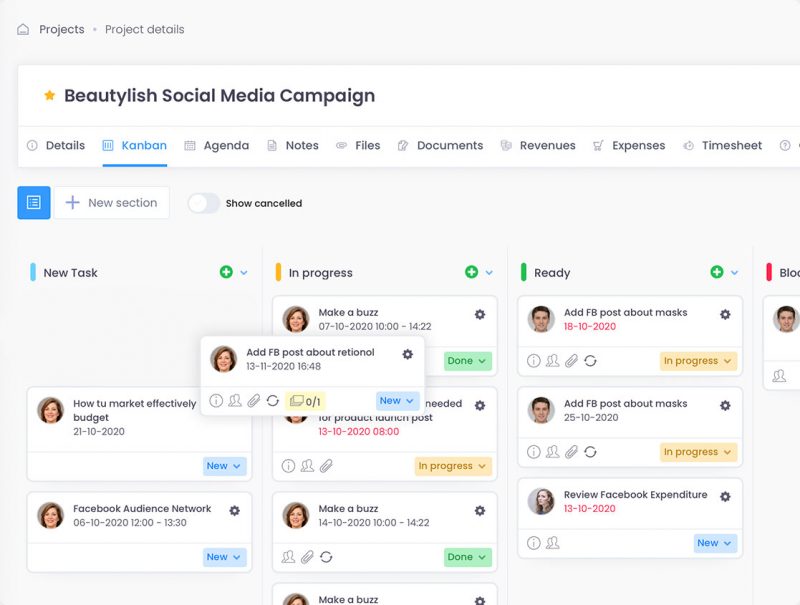
Source: kanban board from a free project management tool: www.firmbee.com
Scrumban
Scrumban, used by 10% of teams, is a combination of Scrum and Kanban in more than just name. Commonly, companies that combine the creation of innovative products with the provision of repeatable services to customers apply it. It has the advantage of reducing the amount of time needed for team communication. Scrumban uses the tenets of Scrum to emphasize the value of improving the work process and constantly adjusting the direction of work to meet customer requirements. On the other hand, it uses Kanban boards, which reduces the amount of time needed to discuss work requirements and results. As a result, follow-up meetings are held every 3 or even 12 months.

Extreme programming (XP)
XP is one of the agile methodologies for implementing IT projects with a high risk of failure. The characteristic feature of project management in the spirit of XP is maximum flexibility and not planning further than necessary. The basic premise of extreme programming, on the other hand, is to improve the quality of the developed software and the quality of life of the people developing it.
The advantage of XP is the constant contact of the team with the client and the ongoing control over the created results, which is achieved by working in pairs. One person performs the assigned tasks, while the other looks at his work asking additional questions and catching errors if necessary. On the other hand, among the disadvantages of extreme programming is, first, that it is very demanding for the client, who must be constantly available to the programming team.
Lean
Lean Management originated just after World War II, based on project management practices developed by Toyota. However, it only gained popularity in the West in the ’90s after the publication of the book The Machine That Changed the World. The main goal of “lean project management” was to reduce waste, that is, to make the best use of a company’s time and resources.
Successful implementation of Lean will significantly reduce the cost of operations, improve efficiency, as well as the quality of products and services. Nowadays, it is mainly used to manage production, and recently it has been increasingly applied to reduce the negative impact of production on the environment.
Prince2
The name Prince2 refers to the project management method and certification for the Projects In Controlled Environments methodology. It focuses on high standardization and repeatability of projects. For this reason, it is used most often in companies that perform repetitive tasks. It allows a precise definition of the project framework and its efficient standardization.
The basic problem with Prince2 has even lived up to its separate abbreviation – PINO, or Prince2 in Name Only. One of its fundamental flaws is its tendency to become increasingly bureaucratic – holding unproductive meetings and creating documents that serve no purpose except for housekeeping purposes.
Six Sigma
Six Sigma originated at Motorola, and is mainly used by large organizations involved in manufacturing. The main goal of this project management method is to improve processes, improve quality and eliminate the frequency of defects in finished products. It is based primarily on data analysis and statistics.
Six Sigma has been criticized for its low emphasis on communication, as a result of which the implemented management changes are often ineffective and do not produce the expected results.
Critical path method (CPM)
The Critical Path Method (CPM) involves creating a project model that includes the following elements:
- tasks necessary to complete the project
- task results
- the amount of time it takes to complete each of them, and
- dependencies between tasks.
CPM is thus about visualizing the entire project and the path to completion. It is often used for project planning and plays a role similar to that of a Gantt chart in the cascading method, or epics in projects managed through agile methodologies.
Critical chain method (CCPM)
The Critical Chain Project Management (CCPM) method is a modification of the CPM method we described above. The key concept here – critical chain – means identifying the longest list of interrelated tasks that need to be completed to complete the project. The CCPM method focuses on resource management and task prioritization. Therefore, it sets much narrower tasks than methodologies such as Scrum, Agile, or the cascade method (Waterfall).
Summary
Project management methods are most often developed by practitioners. Therefore, they usually reflect the needs of a specific organization and respond to challenges that connect to a specific type of activity – services or products, repetitive or unique projects, resource or people management. For this reason, it is advisable to familiarize yourself with existing project management methodologies and consciously choose one or a combination of them that optimally meets the needs of the situation.
If you like our content, join our busy bees community on Facebook, Twitter, LinkedIn, Instagram, YouTube, Pinterest,
Author: Caroline Becker
As a Project Manager, Caroline is an expert in finding new methods to design the best workflows and optimize processes. Her organizational skills and ability to work under time pressure make her the best person to turn complicated projects into reality.
The most important questions
-
Is there one optimal way to manage a project?
The method of management is best chosen not only for the type of tasks performed but also for the capabilities and skills of the Project Manager and the team itself. Therefore, we tend to answer that there is no single right solution.
-
What is the most popular project management method?
Scrum is currently the most popular method applied by the vast majority of teams working in the project system.
Getting started with project management:
- What is a project?
- What is project management?
- How to manage projects?
- Project management methods
- Types of projects
- 4 examples of projects
- Prioritization of projects
- Areas of project activity
- Definition of success in project management
- Why use project management software?
- How to choose the best project management software?
- Overview of project management software
- Project life cycle
- What is the project vision for?
- Project goal. What is it and how to define it well?
- Project initiation phase - what to pay attention to?
- The domain of planning in project management
- What is a project schedule and what is it for?
- How to use milestones in a project?
- Project execution
- How to prepare a successful project contingency plan?
- Importance of project closure
- Project failure. 5 reasons why projects fail
- 4Ps of management: project, product, program and portfolio
- Most important tasks and responsibilities of the Project Manager
- Most useful project manager skills
- How to become a project manager?
- 5 books every project manager should read
- How to set up a project team?
- Work breakdown structure - how to delegate work in a project?
- How to lead a team during hybrid work?
- Challenges project managers face when working with a team
- Types of project meetings
- Project monitoring. What parameters to watch?
- How to write a compelling
- How to define the scope of a project and avoid scope creep?
- Feasibility study – can we implement this project?
- Risk analysis in projects and tools to facilitate it
- How to create a project charter?
- What is a stakeholder register?
- Gantt chart in project management planning
- How to create a project budget?
- Time management in project
- How to create a project risk register?
- Project risk management strategies
- Project marketing
- Sources and areas of change in the project
- Project management change models
- What's after Agile? Methods in project management


















