A favorable situation for the state budget is to increase its revenues, so politicians have taken various measures over the years to achieve this goal. It would seem that the simplest way to do this would be to increase taxation, which would force citizens to contribute more funds to the state. Does it always work that way? Not necessarily, according to Laffer Curve. Read our article to learn more about this phenomenon.
What is the Laffer curve – table of contents:
- What is the Laffer curve – definition
- Causes of the Laffer curve
- Effects of the Laffer curve
- Example of the Laffer curve
- Summary
What is the Laffer curve – definition
The Laffer curve refers to the relationship between the amount of the tax rate and the amount of government revenue. It assumes that an increase in taxes can result in fewer goods being produced, which consequently means less government revenue.
Example graph showing the Laffer curve, source
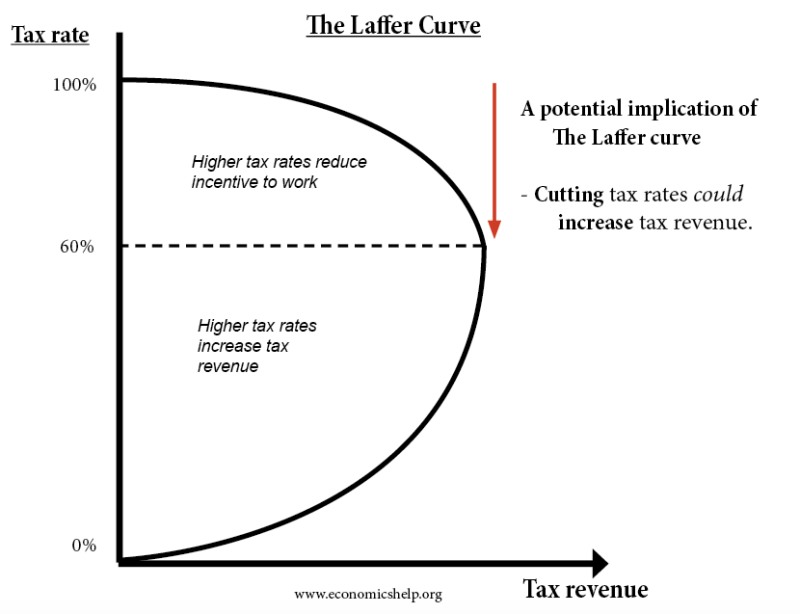
Causes of the Laffer curve
The main reasons for the occurrence are:
- Less motivation to work – when we give the government an increasing percentage of the money we earn, our motivation to work will decrease. As a result, some people will stop working and stop paying taxes on part of their income. For business owners, it’s giving up or stopping some activity that could broaden the tax base.
- Unprofitable hiring – for entrepreneurs who have been striving for profitability until now, the cost of keeping an employee increases and it is no longer profitable. In the long run, no owner can afford to lose financially and is forced to lay off some of his employees to reduce the tax liability associated with their employment.
- Development of the shadow economy – work will begin to be done “in the black”, that is, there will be no taxes. Some products whose prices have increased as a result of the tax increase will be purchased from illegal or hidden production, which will reduce the volume of taxable turnover.
Effects of the Laffer curve
Reducing tax rates can carry different effects – economic, arithmetic, income or substitution
- Economic effect
- Arithmetic effect
- Income effect
- Substitution effect
It is long-term in nature. Lower taxes contribute to higher incomes, encouraging more consumption. As a result, rising demand stimulates the economy – production increases, employment increases, and people are more willing to invest.
Any reduction in tax dues means less revenue for the state, reducing the power of the stimulative function of taxes.
Higher public tributes reduce the final salary that workers receive. People may feel the need to work more to earn the expected income.
Another scenario is that employees may feel discouraged by lower salaries and will not see the point in working harder.
Example of the Laffer curve
Below we will present an example of an economic situation when this phenomenon occurred in the USA :
In the 1980s, property taxes were cut by more than half in California. Tax rates fell from 70% to 28%, which at the same time resulted in a 28% increase in revenue to the US budget. It also showed that tax reforms most often hit the wealthiest taxpayers. Their share rose from 18% to 15.6%. In contrast, almost half of the less affluent population paid less, dropping from 7.4% to 5.7%.
Other noticeable effects of the reduction in existing tax dues in the United States have been to increase labor supply by about 2% and encourage the public to invest more.
However, due to the change in power in the US, it was decided in 1990 to raise the personal income tax from 28% to 31%. It turned out, however, that despite the increase in the tax rate, a smaller share of income tax in the state budget was recorded a year later.

Summary
Based on the above correlations, it is easy to see that raising tax rates too much will not necessarily have a positive effect on the economy. Increasing the resources of the state budget is assumed in theory. At the same time, reality shows that social attitudes also play a big role, and the effects of political decisions are often unpredictable. When introducing higher fees, one should expect dissatisfaction among citizens, who will sooner or later look for ways to avoid worsening their economic situation.
Read also: What is web scraping and how to use it in business?
If you like our content, join our busy bees community on Facebook, Twitter, LinkedIn, Instagram, YouTube, Pinterest, TikTok.
Author: Andy Nichols
A problem solver with 5 different degrees and endless reserves of motivation. This makes him a perfect Business Owner & Manager. When searching for employees and partners, openness and curiosity of the world are qualities he values the most.


















