Herzberg’s motivation theory is well-know concept, sometimes called dual-factor theory or two-factor theory. Accordingly to the psychology of motivation work engagement of employees depends on many different factors. Employer may use various incentives to influence his workers but some actions may bring adverse results. What then is the best way to motivate employees to increase job satisfaction and bring benefits for the employer?
Herzberg’s motivation theory – table of contents:
Herzberg’s motivation theory
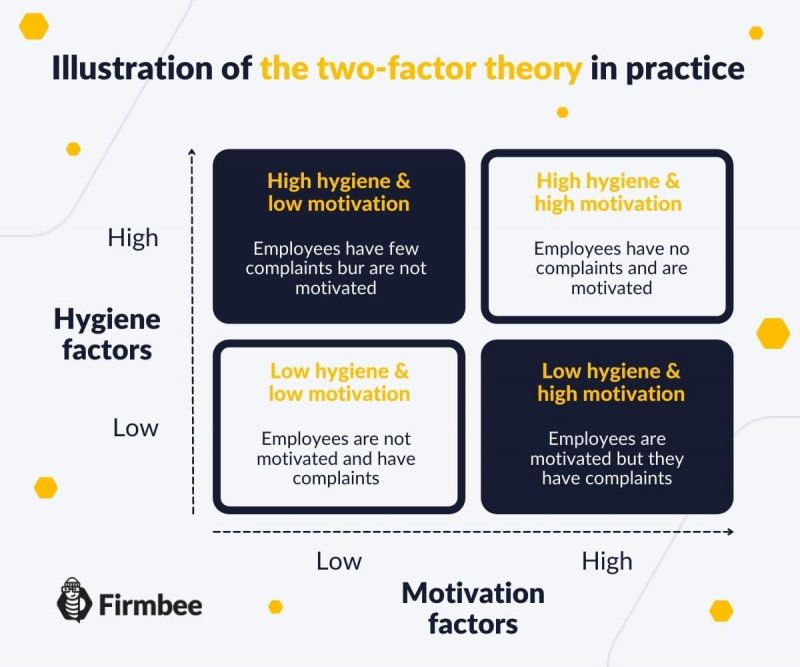
Psychologist Frederick Herzberg developed his model of theory of motivation in 1959. As a result of his research he presented conception called: The two-factor theory of motivation. In this model there are two types of factors that influence motivation in the workplace: basic hygiene factors and higher-order motivating factors.
Hygiene factors (internal)
Hygiene factors are sources of motivation related to the workplace itself. Lack of attention to the hygiene factors causes dissatisfaction at the workplace, while prevention from discontentment does not provide positive motivation. There are several hygiene factors such as:
- Working conditions – functionality and comfort of work
- Interpersonal relations between employees, departments, and management
- Remuneration – salary and benefits
- Job security – sense of stability of employment
- Influence on employees private life and ability to provide proper standard of living
- Quality of management and relationship with supervisor
- Company policies, rules and administration
Motivator factors (external)
Motivational factors are related with the work itself and improvements made in the area of motivational factors enhance work satisfaction, while lack of care for external factors sphere does not bring dissatisfaction of the employee. The list of motivational factor comprises:
- Recognition – efforts should be noticed and appreciated by the employer to reinforce good performance
- Responsibility – employee should have certain level of control over own activities
- Job advancement opportunities – ability to reach higher levels on the career ladder and to improve conditions of living
- Sense of achievement – employee have to be able to finalize assignments and achieve goals
- Growth opportunities – chances for professional development and upskilling
Only after altering all hygiene factors company may concentrate on motivational factors. Addressing motivational factors will not be effective as long as the employees will experience high level of job dissatisfaction and stress related to work.

The application of Herzberg’s motivation
Herzberg’s theory of motivation explains that hygiene factors are not able to increase satisfaction of the individuals and constant improvement of working conditions won’t boost productivity. Therefore employer should regularly examine levels of dissatisfaction among his employees. Establishment of external factors (motivators) may start after the level of dissatisfaction among employees equals zero.
To achieve intended effects regarding motivation employer should constantly pay attention to the hygiene factors and provide appropriate work conditions. When the work hygiene is granted all motivator factors may be used to motivate workers for the joined benefit of all parties.
Read also: Top tips to stay motivated at work
If you like our content, join our busy bees community on Facebook, Twitter and Linkedin.
Author: Nicole Mankin
HR manager with an excellent ability to build a positive atmosphere and create a valuable environment for employees. She loves to see the potential of talented people and mobilize them to develop.


















