Experiential learning in the workplace helps people improve the skills they need to do their jobs. It involves detecting and eliminating mistakes, and helps to get a new perspective on work. Employees can either learn on their own or from others. Although the experiential learning method was developed in 1974 by David Kolb – an American scientist, it is still eagerly implemented by organizations. What is experiential learning? What is Kolb’s learning cycle? Read our article to find out.
Experiential learning – table of contents:
What is experiential learning?
Experiential learning involves analyzing your own professional experiences and establishing a plan to apply them to your work. This process should be supported by managers, team leaders and colleagues. Therefore, good communication is so important in this case.
The difference between theory-based learning and practice-based learning is huge, and this is best illustrated by Mel Silberman (the author of “Active Training: A Handbook of Techniques, Designs Case Examples, and Tips”);
- What I hear, I forget,
- What I hear and see, I remember a little,
- What I hear, see, and ask questions about or discuss with someone else, I begin to understand,
- What I hear, see, discuss, and do, I acquire knowledge and skill,
- What I teach to another, I master.
David Kolb’s learning cycle
A similar approach was presented by David Kolb, who developed a theory of experiential learning called Kolb’s cycle. The key element of this model is to develop practical skills, experience and critical thinking. Although his methodology does not provide a set of ready-made recommendations and advice, it points to mechanisms that foster effective learning.
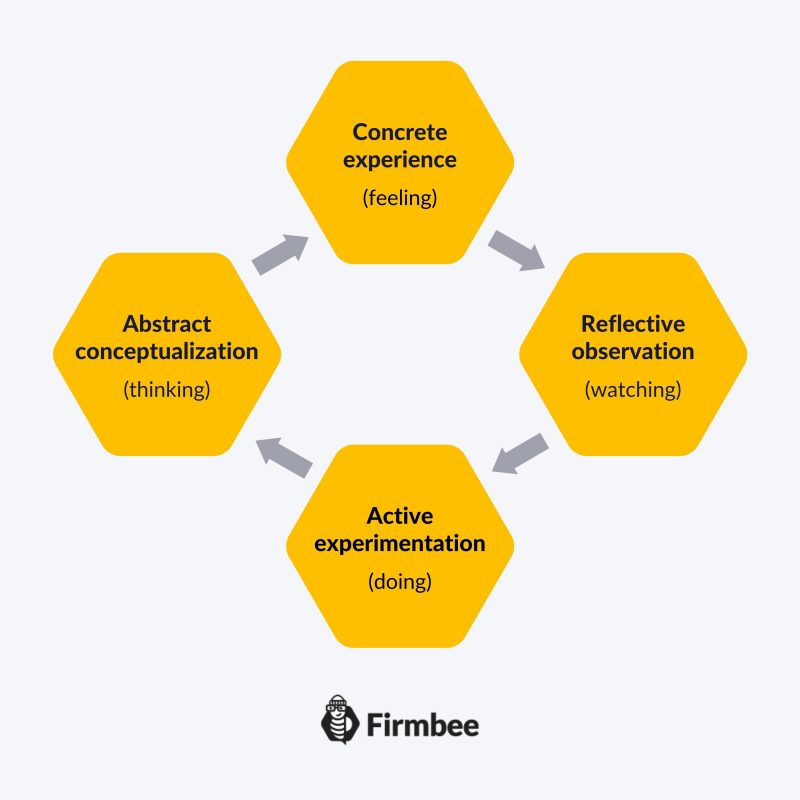
The experiential learning cycle consists of four stages:
- Concrete experience (feeling) – planned or accidental, what we do and feel at a given moment,
- Reflective observation (watching) – analyzing the experience and determining its importance,
- Abstract conceptualization (thinking) – creating various concepts and ideas that could be implemented in similar situations,
- Active experimentation (doing) – testing ideas and concepts in new situations.
According to Kolb, when we learn something new, we modify our past experiences, and this in turn affects our subsequent actions. We refer to this process as a repetitive sequence – once the last stage is completed, the next one begins.
Learning styles
Each person prefers a different way of learning. Therefore, Kolb defined the following learning styles to help trainers in adapting their teaching methods:
- Diverging. Individuals with the diverging style are sensitive and creative. They like collecting information, and are able to look at situations from various perspectives.
- Assimilating. People with the assimilating learning preference are more interested in ideas and abstract concepts. There are good at analyzing and organizing information in a clear and logical way.
- Converging. The converging learning style involves a practical approach. People with the converging learning style like experimenting with ideas and searching for useful solutions to check if a theory will work in practice.
- Accommodating. This is a prevalent learning style. Individuals with the accommodating learning preferences rely on intuition rather than logic.
Another classification of learning preferences was proposed by Honey and Mumford:
- Activists. They enjoy new challenges and fully engage in new experiences. They learn best when they are thrown in at the deep end, and when they work in teams and experiment.
- Reflectors. Reflectors stand by, observe, collect data, and carefully draw conclusions. They need to have time to make decisions based on careful analysis.
- Theorists. Theorists strive for perfection. They like asking questions and must have clearly defined goals.
- Pragmatists. They test new ideas, concepts and methods in practice. They must see the connection between theory and practice, as well as prefer concrete examples and feedback.
Summary
The experiential learning model proposed by Kolb seems to be an extremely effective learning method that allows employees and organizations to grow. However, some HR specialists belittle this learning style, mainly because of the fact that it rejects the theoretical basis. Nevertheless, Kolb’s cycle is the foundation for most knowledge management theories, and is excellent for business coaching.
Other resources: 6 strategies to promote inclusion in the workplace.
If you like our content, join our busy bees community on Facebook, Twitter, LinkedIn, Instagram, YouTube, Pinterest.
Author: Nicole Mankin
HR manager with an excellent ability to build a positive atmosphere and create a valuable environment for employees. She loves to see the potential of talented people and mobilize them to develop.